Vitess 샤딩 과정
1. 샤딩 개요
샤드 0(단일 샤드)에 부하가 발생하여 샤딩을 수행합니다. 새로운 샤드 -80, 80-을 생성하고, 트래픽을 점진적으로 이전한 후 기존 샤드를 삭제합니다.
2. 환경 설정 및 샤드 추가
source ../common/env.sh
env.sh 파일을 불러와 환경 변수를 설정합니다.
샤드 -80을 위한 MySQL 및 vttablet 실행
for i in 300 301 302; do
CELL=zone1 TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/mysqlctl-up.sh
CELL=zone1 KEYSPACE=customer TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/vttablet-up.sh
done
300~302는 -80 샤드를 위한 MySQL 및 vttablet을 실행하는 태블릿 ID입니다.
샤드 80-을 위한 MySQL 및 vttablet 실행
for i in 400 401 402; do
CELL=zone1 TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/mysqlctl-up.sh
CELL=zone1 KEYSPACE=customer TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/vttablet-up.sh
done
400~402는 80- 샤드를 위한 MySQL 및 vttablet을 실행하는 태블릿 ID입니다.
잠깐! -80, 80- 이 의미하는 것
Vitess에서 샤딩할 때 -80, 80-과 같은 표현은 해시 키 범위를 나타냅니다.
여기서 80은 16진수(HEX) 표현으로, 10진수로 변환하면 128(10진수) 입니다.
- -80 → 해시 값이 0x00(0)부터 0x80(128)까지의 데이터는 첫 번째 샤드에 저장
- 80- → 해시 값이 0x80(128)부터 0xFF(255)까지의 데이터는 두 번째 샤드에 저장
샤딩 키와 데이터 분배
샤딩을 적용할 때, 샤딩 키(Sharding Key) 를 기준으로 데이터를 어떤 샤드에 저장할지 결정합니다.
샤딩 키는 일반적으로 id 같은 고유 값이 될 수 있습니다.
Vitess는 샤딩 키를 해시(Hash) 함수에 넣어 해시 값을 만든 후, 이 값이 -80 범위인지 80- 범위인지 확인하여 샤드를 선택합니다.
예를 들어:
- INSERT INTO users (id, name) VALUES (101, 'Alice');
- 101의 해시 값이 0x50(80보다 작음) → 첫 번째 샤드(-80)에 저장
- INSERT INTO users (id, name) VALUES (202, 'Bob');
- 202의 해시 값이 0xA0(80보다 큼) → 두 번째 샤드(80-)에 저장
정리
✅ -80, 80-은 샤딩 키 해시 값의 범위를 나누는 기준
✅ 샤딩 키를 해싱하여 데이터가 어느 샤드로 가야 할지 자동으로 결정됨
3. 샤드 상태 확인
for shard in "-80" "80-"; do
wait_for_healthy_shard customer "${shard}" || exit 1
done;
각 샤드의 상태가 healthy 상태가 될 때까지 대기합니다.
샤드 생성 완료

# 현재 생성된 샤드에는 table이 아무것도 없음
mysql> use customer/-80
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use customer/80-
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
Empty set (0.01 sec)
4. Resharding 트래픽 전환
- switchtraffic 전 주의사항:
- 소스 샤드와 타겟 샤드의 데이터가 동기화 되었는지 확인
- 애플리케이션에서 새로운 샤드로의 트래픽 전환 테스트
1) Reshard 워크 플로우 생성
vtctldclient Reshard --target-keyspace customer --workflow cust2cust create --source-shards '0' --target-shards '-80,80-'
- source-shards '0' → 기존 샤드에서 데이터를 이동
- target-shards '-80,80-' → 새 샤드로 데이터를 재분배
- customer/0에서 customer/-80와 customer/80-로 분배된다는 뜻
- 80은 0에서 80보다 작은 값들의 범위를 다룹니다.
- 80-은 80 이상의 값들을 다룹니다.
# 아래 DB 정보를 보면 테이블도 생성 되고 데이터도 분배되어 등록된 부분을 확인 할 수 있음
mysql> use customer/80-
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+-----------------------+
| Tables_in_vt_customer |
+-----------------------+
| corder |
| customer |
+-----------------------+
2 rows in set (0.07 sec)
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+--------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+--------------------+
| 1 | alice@domain.com |
| 2 | bob@domain.com |
| 3 | charlie@domain.com |
| 4 | dan@domain.com |
| 5 | eve@domain.com |
| 1000 | jack@domain.com |
+-------------+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use customer/-80
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+-----------------------+
| Tables_in_vt_customer |
+-----------------------+
| corder |
| customer |
+-----------------------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+------------------+
| 1001 | teemo@domain.com |
+-------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
1) rdonly 및 replica 트래픽 전환
vtctldclient Reshard --workflow cust2cust --target-keyspace customer switchtraffic --tablet-types "rdonly,replica"
우선 rdonly 및 replica 트래픽을 새로운 샤드로 전환하여 읽기 요청을 새로운 샤드에서 처리할 수 있도록 합니다.
2) primary 트래픽 전환
vtctldclient Reshard --workflow cust2cust --target-keyspace customer switchtraffic --tablet-types "primary"
마지막으로 primary 트래픽을 새로운 샤드로 전환하면, 기존 샤드는 더 이상 트래픽을 처리하지 않습니다.
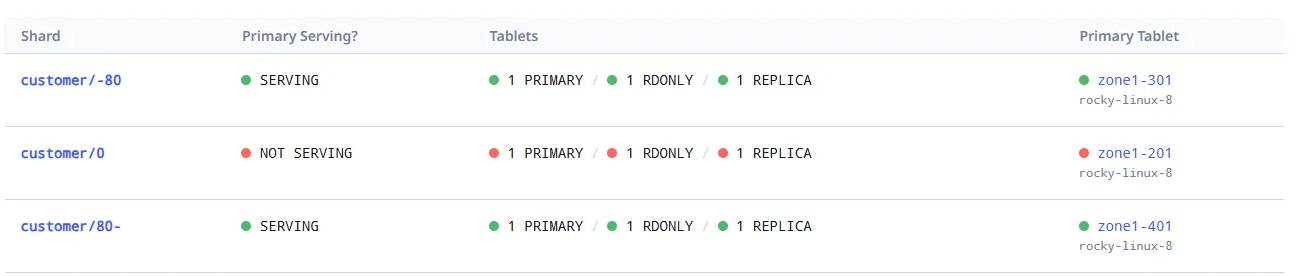
트래픽 전환 전 (0번 샤드가 SERVING 중)

트래픽 전환 후 (0번 샤드는 NOT SERVING 상태, 트래픽 중지)
3) complete 를 하여 Reshard 작업을 마무리
vtctldclient Reshard --workflow cust2cust --target-keyspace customer complete
여기까지 작업이 완료 되면 shard/0 은 비활성화 됩니다.

더 이상 필요하지 않은 200~202 vttablet 과 mysql 인스턴스를 중지 합니다.
for i in 200 201 202; do
CELL=zone1 TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/vttablet-down.sh
CELL=zone1 TABLET_UID=$i ../common/scripts/mysqlctl-down.sh
done
5. MySQL 데이터 확인
샤드 80- 데이터 확인
mysql> use customer/80-;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+--------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+--------------------+
| 1 | alice@domain.com |
| 2 | bob@domain.com |
| 3 | charlie@domain.com |
| 4 | dan@domain.com |
| 5 | eve@domain.com |
| 1000 | jack@domain.com |
+-------------+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
customer/80- 샤드에서 customer 테이블 데이터를 확인합니다.
샤드 -80 데이터 확인
mysql> use customer/-80;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+------------------+
| 1001 | teemo@domain.com |
+-------------+------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
customer/-80 샤드에서 customer 테이블 데이터를 확인합니다.
6. 데이터 삽입 및 분배 테스트
mysql> insert into customer (email) values ('kim@domain.com');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> insert into customer (email) values ('sim@domain.com');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> insert into customer (email) values ('lee@domain.com');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+--------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+--------------------+
| 1001 | teemo@domain.com |
| 1101 | sim@domain.com |
| 1 | alice@domain.com |
| 2 | bob@domain.com |
| 3 | charlie@domain.com |
| 4 | dan@domain.com |
| 5 | eve@domain.com |
| 1000 | jack@domain.com |
| 1100 | kim@domain.com |
| 1102 | lee@domain.com |
+-------------+--------------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use customer/-80;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+------------------+
| 1001 | teemo@domain.com |
| 1101 | sim@domain.com |
+-------------+------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use customer/80-;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from customer;
+-------------+--------------------+
| customer_id | email |
+-------------+--------------------+
| 1 | alice@domain.com |
| 2 | bob@domain.com |
| 3 | charlie@domain.com |
| 4 | dan@domain.com |
| 5 | eve@domain.com |
| 1000 | jack@domain.com |
| 1100 | kim@domain.com |
| 1102 | lee@domain.com |
+-------------+--------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
8. 마무리
Vitess의 Resharding 과정을 통해 부하를 분산하고 새로운 샤드로 데이터를 정상적으로 이전하는 것을 확인하였습니다.
'기술, 개발 > Vitess' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Vitess 수평 샤딩 1 (시퀀스) (0) | 2025.08.28 |
|---|---|
| Vitess MoveTables (수직샤딩) (1) | 2025.08.28 |
| vtctld, vtgate, vttablet, vtorc (0) | 2025.08.28 |
| Vitess 기본 개념 (0) | 2025.08.28 |
| 로키리눅스 vitess 설치 (0) | 2025.08.28 |